Computes outlier persistence for a range of significance values.
Source:R/outlier_persistence.R
persisting_outliers.RdThis function computes outlier persistence for a range of significance values, using the algorithm lookout, an outlier detection method that uses leave-one-out kernel density estimates and generalized Pareto distributions to find outliers.
Usage
persisting_outliers(
X,
alpha = seq(0.01, 0.1, by = 0.01),
st_qq = 0.9,
scale = TRUE,
num_steps = 20,
old_version = FALSE
)Arguments
- X
The input data in a matrix, data.frame, or tibble format. All columns should be numeric.
- alpha
Grid of significance levels.
- st_qq
The starting quantile for death radii sequence. This will be used to compute the starting bandwidth value.
- scale
If
TRUE, the data is scaled. Default isTRUE. Which scaling method is used depends on theold_versionparameter. Seelookoutfor details.- num_steps
The length of the bandwidth sequence.
- old_version
Logical indicator of which version of the algorithm to use.
Value
A list with the following components:
outA 3D array of
N x num_steps x num_alphawhereNdenotes the number of observations,num_stepsdenote the length of the bandwidth sequence, andnum_alphadenotes the number of significance levels. This is a binary array and the entries are set to 1 if that observation is an outlier for that particular bandwidth and significance level.bwThe set of bandwidth values.
gpdparasThe GPD parameters used.
lookoutbwThe bandwidth chosen by the algorithm
lookoutusing persistent homology.
Examples
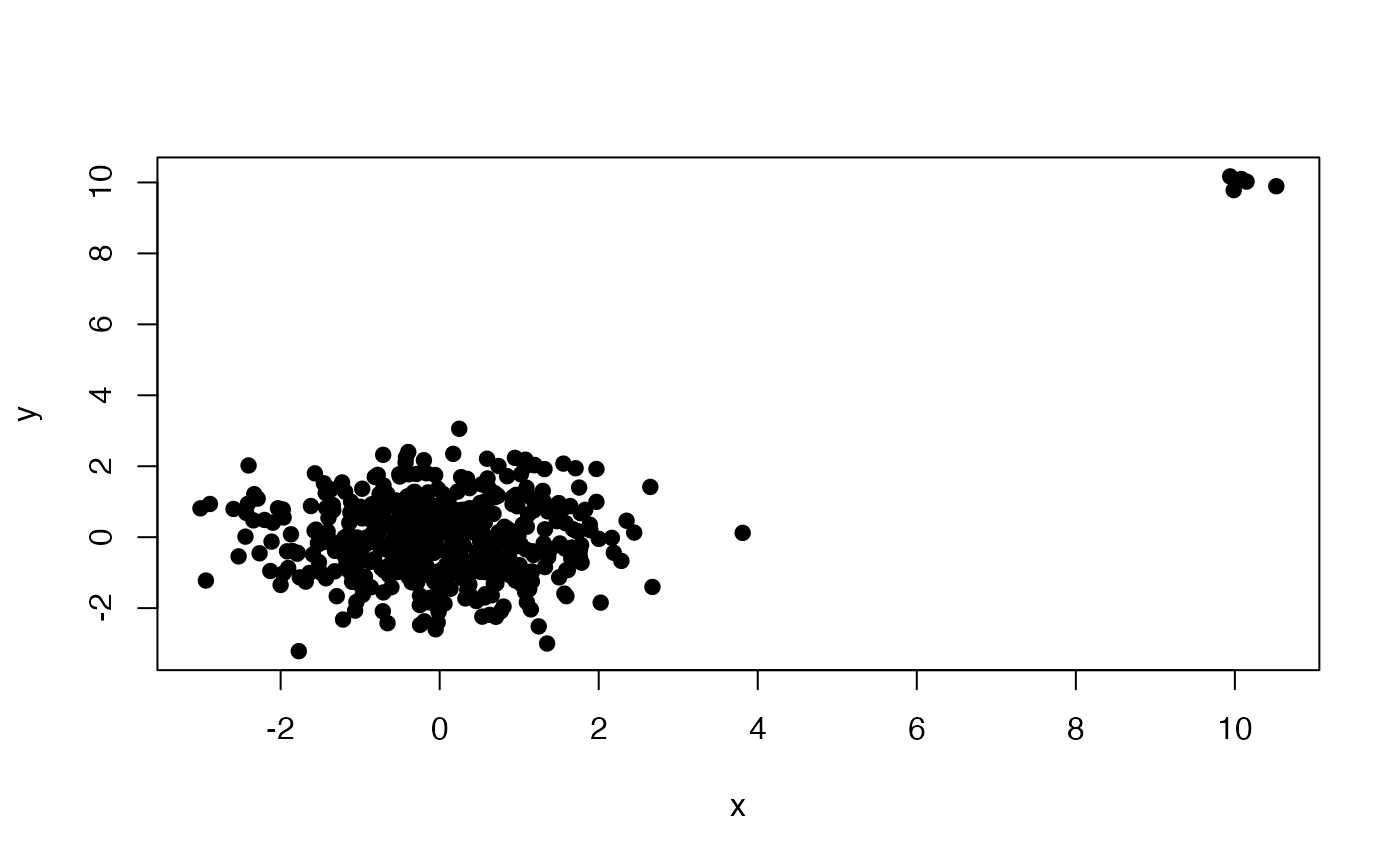
X <- rbind(
data.frame(
x = rnorm(500),
y = rnorm(500)
),
data.frame(
x = rnorm(5, mean = 10, sd = 0.2),
y = rnorm(5, mean = 10, sd = 0.2)
)
)
plot(X, pch = 19)
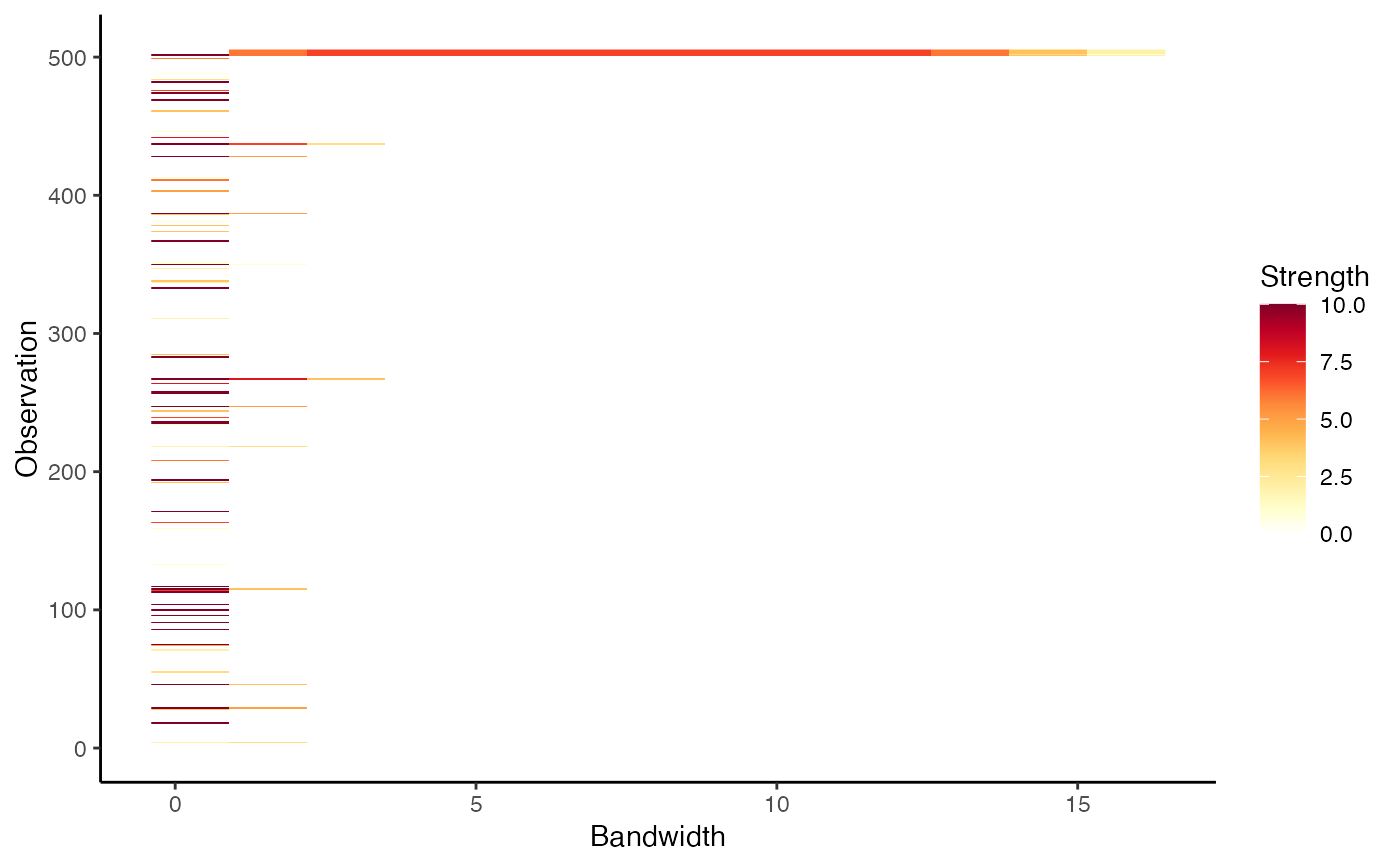
 outliers <- persisting_outliers(X, scale = FALSE)
outliers
#> Persistent outliers using lookout algorithm
#>
#> Call: persisting_outliers(X = X, scale = FALSE)
#>
#> Lookout bandwidth: 3.049485
autoplot(outliers)
outliers <- persisting_outliers(X, scale = FALSE)
outliers
#> Persistent outliers using lookout algorithm
#>
#> Call: persisting_outliers(X = X, scale = FALSE)
#>
#> Lookout bandwidth: 3.049485
autoplot(outliers)